Chlorogenic Acid (CGA)
Introduction
Chlorogenic acids (CGAs), a group of phenolic esters of caffeic and ferulic acids, are found in many plants, fruits, and vegetables. They are reported to be found in high concentrations in coffee, as high as 70-350 mg per cup of coffee. More than 80 different CGAs were detected in green coffee beans, with 5-caffeoylquinic acid being the most abundant.(1)
The degree of roasting and geographical origin of coffee beans were shown to affect the CGA content. The higher the roasting degree, the lower the CGA content as it is decomposed with exposure to heat, therefore a negative correlation between the CGA levels with the degree of roasting, with the highest content of CGA content, 543.23 mg/L, found in the green coffee.(1) Antioxidant effects of coffee samples were largely determined by CGA content.(1)
Health Effect
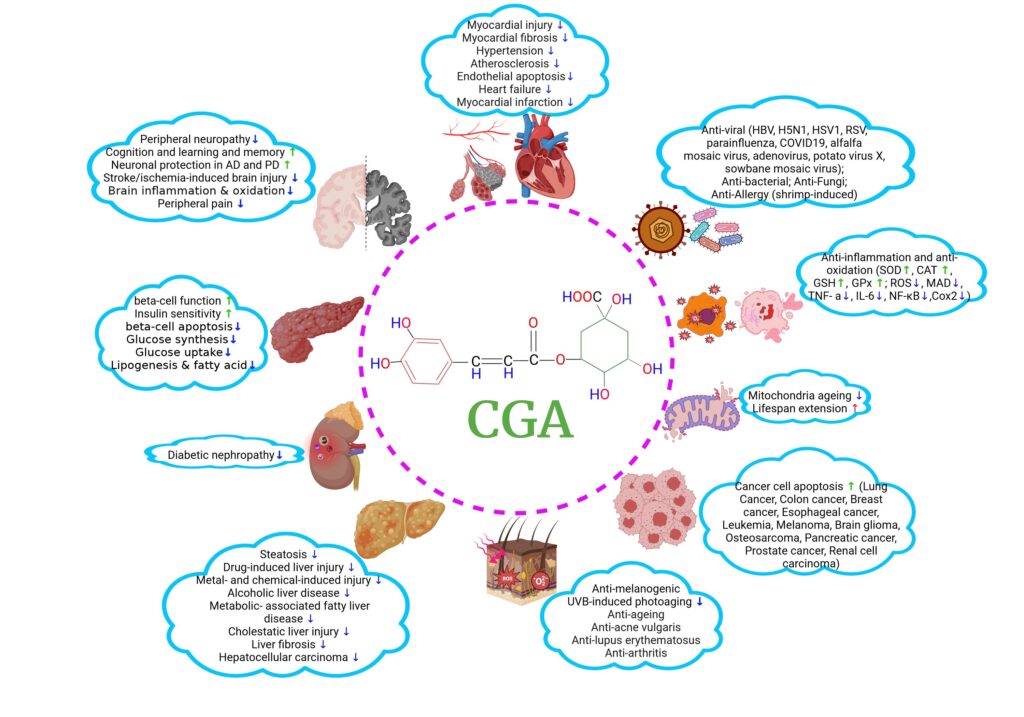
CGA shows various beneficial roles in many pathological conditions, including modulation of glucose and lipid homeostasis, recovery from neurological impairments such as neurodegenerative disorders and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, mitigation of DM and its complications, protection of cardiovascular system, liver, lungs, kidney, and skin, anti-pathogens, and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation and migration.(2)
Mechanism
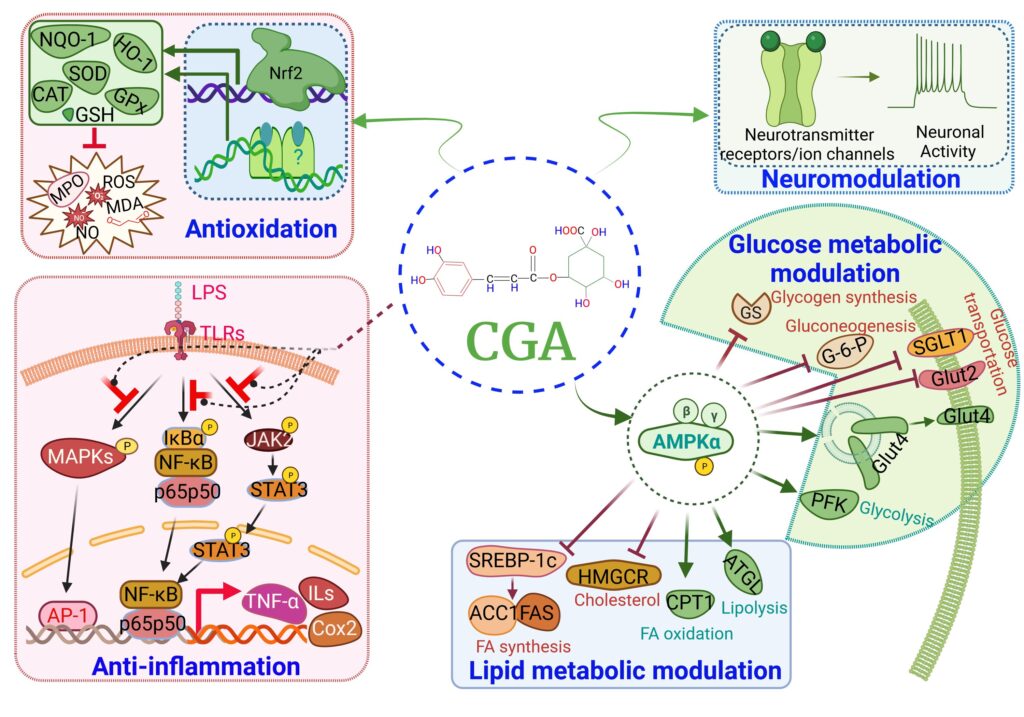
CGA can potentially 1) target NF-kB, MPAKs and JAK pathways to mitigate inflammation; 2) activate Nrf2-depednent and independent pathways to execute antioxidation function; 3) exhibit neuromodulation through targeting neuroreceptors and ion channels; 4) modulate glucose metabolism through increasing glycolysis and suppressing glucose uptake and glucose synthesis; and 5) regulate lipid metabolism through increasing lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation and suppressing synthesis of cholesterol and fatty acids.(2)
Safety
CGA exhibits a good safety profile, which has not shown any obvious adverse effect and toxicity to normal cells or tissues and is well-tolerated by humans.(2) CGA intake for weeks to months or at higher dosages does not render any side effect or toxicity in animals, though very high dosage consumption of CGA moderately increases plasma homocysteine levels in humans.(2)
Reference
- Awwad S, Issa R, Alnsour L, Albals D, Al-Momani I. Quantification of Caffeine and Chlorogenic Acid in Green and Roasted Coffee Samples Using HPLC-DAD and Evaluation of the Effect of Degree of Roasting on Their Levels. Molecules. 2021 Dec 11;26(24):7502. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247502. PMID: 34946584; PMCID: PMC8705492.
- Nguyen V, Taine EG, Meng D, Cui T, Tan W. Chlorogenic Acid: A Systematic Review on the Biological Functions, Mechanistic Actions, and Therapeutic Potentials. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070924.
